2nd CubeSat Design and Development Competition Conducted by Iran
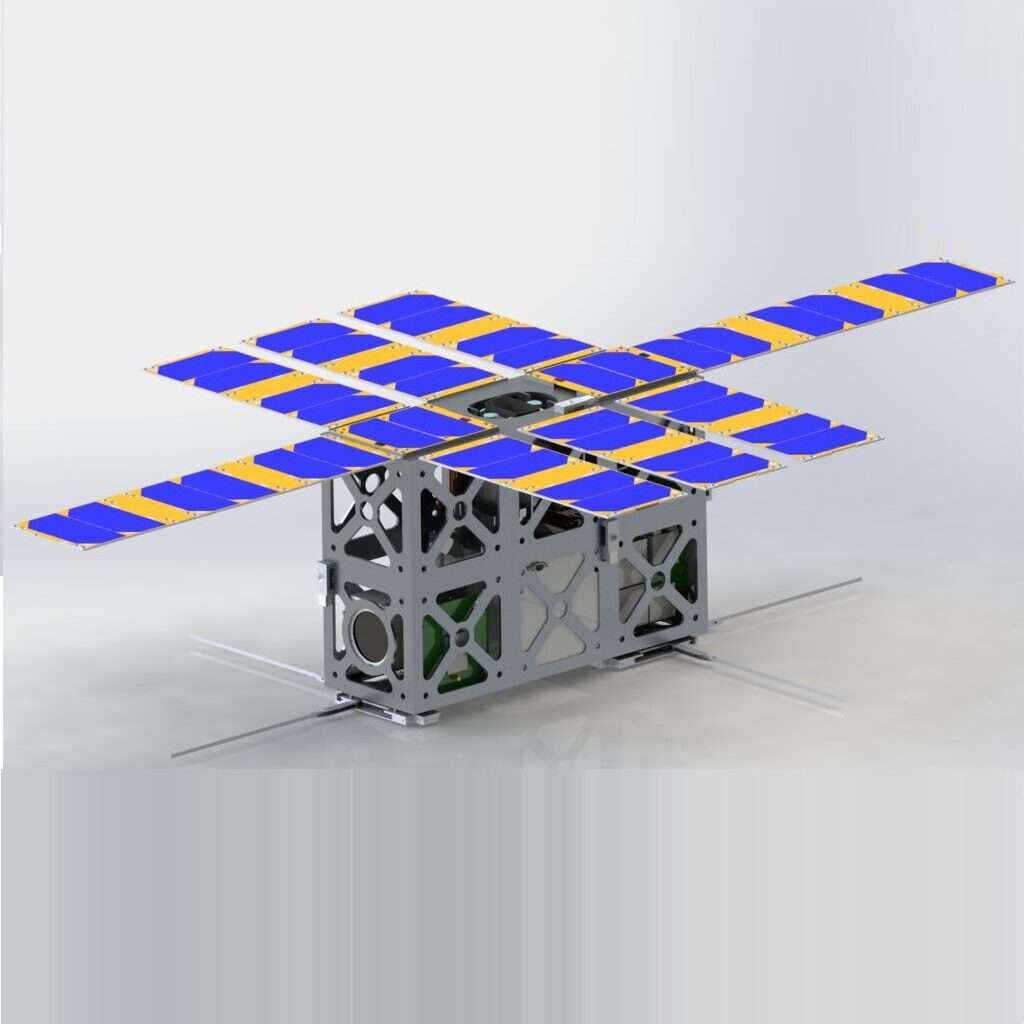
Initial design and analysis have been conducted for a 6U CubeSat with the goal to design of the constellation with the 3-5 number of CubeSats to achieve its maximum surface coverage area. The study focused on the different elevation angles and it has observed that the elevation angle of 5 degree and altitude of 600 km, one can have the 5 orbital planes to placed their CubeSats and each CubeSats can be placed in different orbital planes with the different true anolomy values to avoid any interferences.
The work continues to obtain the characteristics and setup using software and different simulations platform which help model the satellite’s projected trajectory, structural and thermal properties, and detumbling method. Test plans and a budget sheet were then created to keep track of the costs throughout the mission.
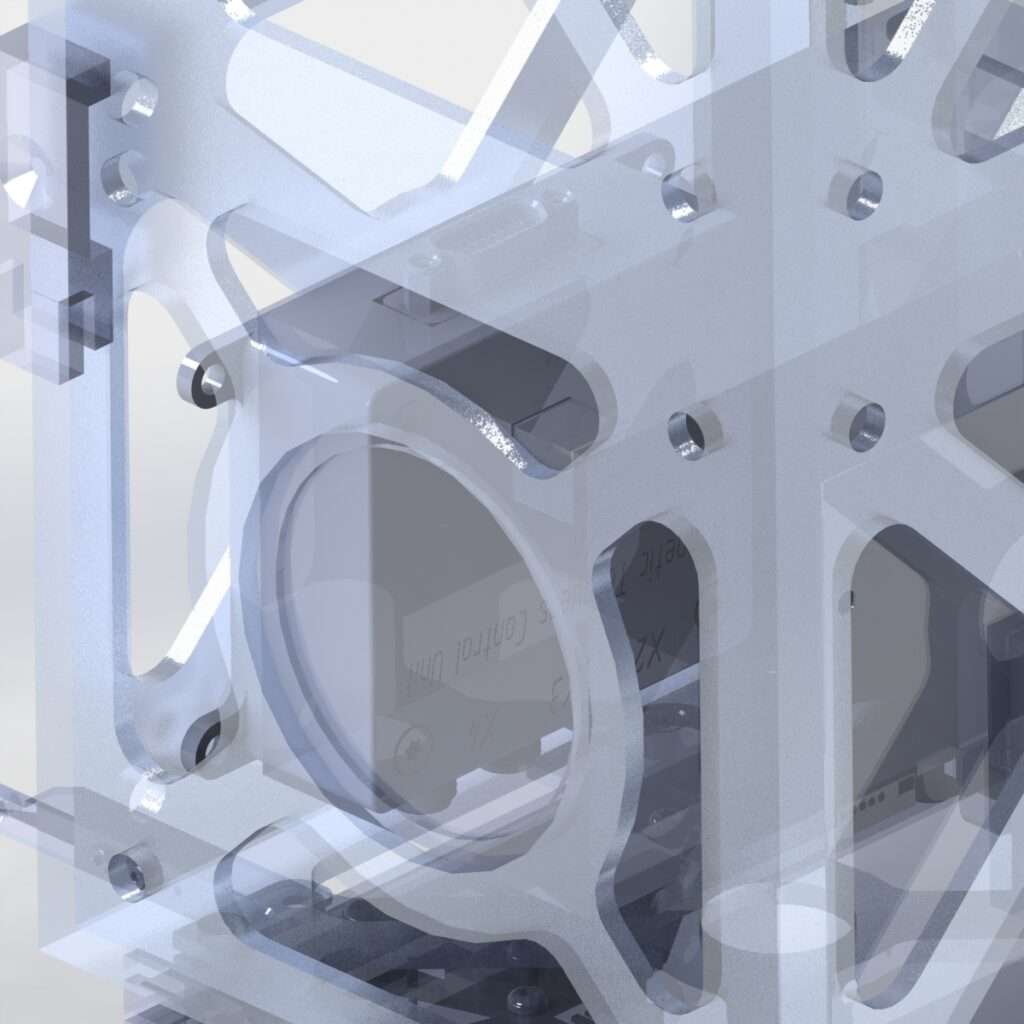
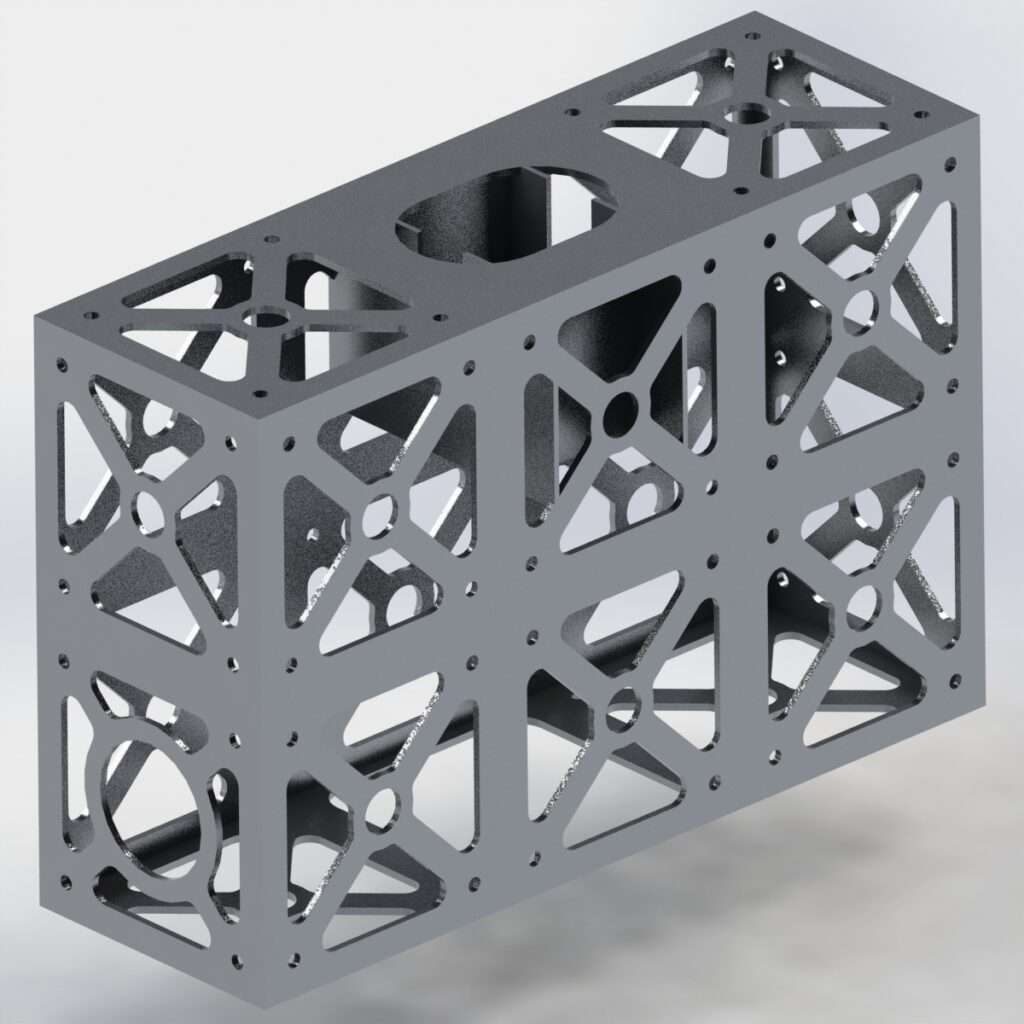
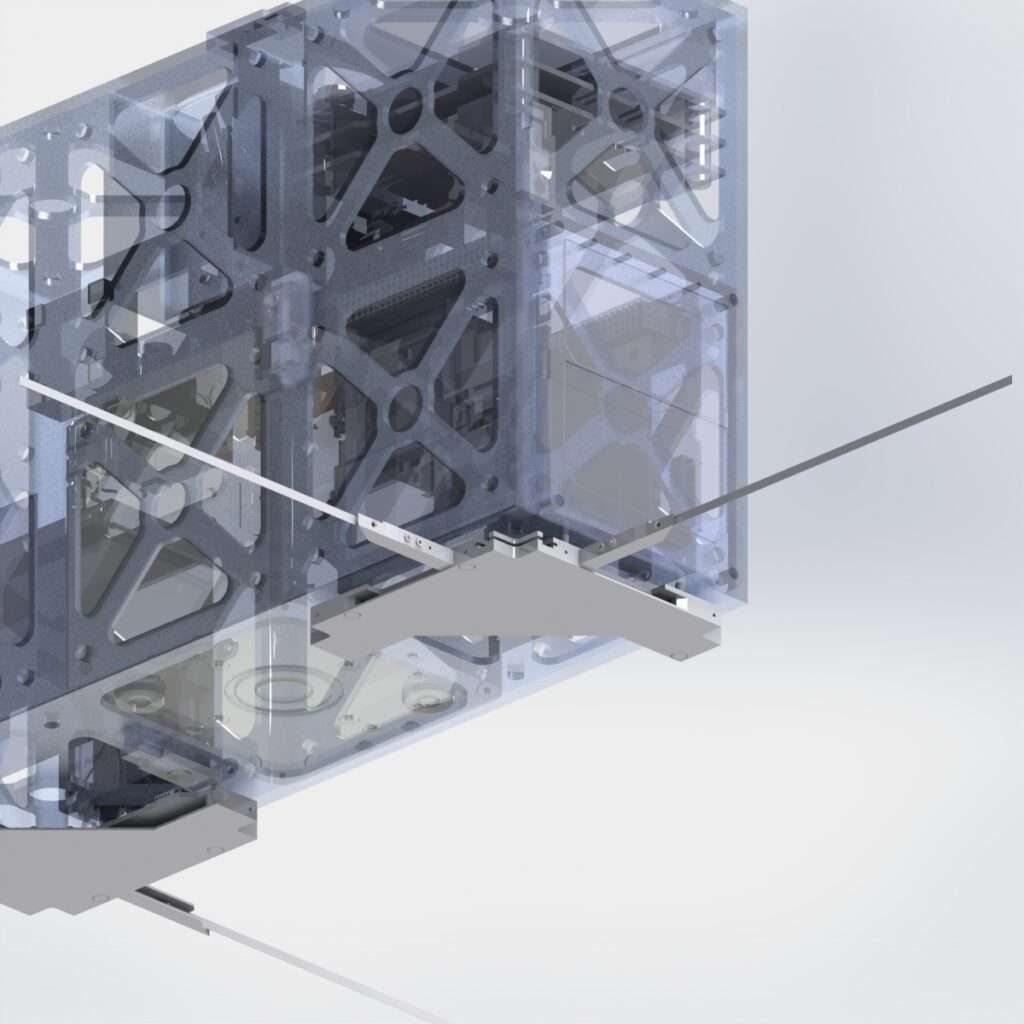
CubeSats are a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites. CubeSats are built to standard dimensions (Units or “U”) of 10 cm x 10 cm x 10 cm. They can be 1U, 2U, 3U, or 6U in size, and typically weigh less than 1.33 kg (3 lbs) per U. NASA’s CubeSats are deployed from a Poly-Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD
NASA’s CubeSat Launch initiative (CSLI) provides opportunities for small satellite payloads to fly on rockets planned for upcoming launches. These CubeSats are flown as auxiliary payloads on previously planned missions.
The cube-shaped satellites are approximately four inches long, have a volume of about one quart and weigh about 3 pounds. To participate in the CSLI program, CubeSat investigations should be consistent with NASA’s Strategic Plan and the Education Strategic Coordination Framework. The research should address aspects of science, exploration, technology development, education or operations.
Some CubeSats have become countries’ first-ever satellites, being launched by universities, state-owned, or private companies. The searchable Nanosatellite and CubeSat Database lists over 3,200 CubeSats that have been and are planned to be launched since 1998.[4]
Constellation Design of Three to Five Satellites in LEO Orbit to Established the Communication from Ground

The design of a constellation is an important aspect from the coverage point of view to efficient use of a CubeSat. For the global coverage, there are many CubeSats required for low earth orbit (LEO) constellation design. However, in this work only 3-5 number of CubeSats has been used to design the LEO constellation to cover the limited area of interest. The study has been focuses on the different elevation angles and it has observed that the elevation angle of 5 degree and altitude of 600 km, one can have the 5 orbital planes to placed their CubeSats and each CubeSats can be placed in each orbital planes. The Maximum coverage area of constellation has been achieved with the 5 number of CubeSats and its value is 6.23×107 Km2at the corresponding earth’s central angle of 18 degree and the corresponding coverage percentage of 2.44 % has been found.
OUR MISSION
- Miniaturization or mass and power reduction of platform and instruments
- Cost reduction through novel launching strategies, mission planning and usage of the ground networks.